Original Article
Year: 2021 |Volume: 2 | Issue: 10 |Pages: 45-53
Interstitial Cystitis (IC) -Ayurvedic Approach
About Author
Correspondence Address:
Dr Shilpa Premchand Badhe HOD, Professor, Dept of Shalyatantra SMBT Ayurved College & Hospital,Igatpuri,Nashik C-304,Sai Anand Pride Nasikroad,Nashik-422101 Email- adkpc74@gmail.com Mobile no.9689339928
Date of Acceptance: 2021-11-03
Date of Publication:2021-11-22
Article-ID:IJIM_109_11_21 http://ijim.co.in
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared
How To Cite This Article: Badhe SP. Interstitial Cystitis (IC) -Ayurvedic Approach. Int J Ind Med 2021;2(10):45-53
Abstract
Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition resulting in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder or surrounding pelvic region. People with IC usually have inflamed or irritated bladder walls which can cause scarring and stiffening of the bladder. IC affects men and women of all racial and ethnic backgrounds and ages. However, it is more common in women than men. This condition is very much painful, difficult to explain and tolerate especially for working female in India. Also due to lack of facilities, cleanliness, and unhygienic conditions it’s very hard to prevent. Treatment for IC in modern medicine is anti-inflammatory and Antibiotics. There is increasing resistance towards available antibiotics. Hence everyone is searching for better option with better result and within the reach of common people. We conducted a clinical trial on 60 patients of age from 30 to 50 years. We gave trial for Doorvadi tail Uttarbasti for 3 days in Mootrakriccha.
Keywords: Doorvadi tail, Uttarbasti, mootrakriccha, Interstitial Cystitis
Introduction
In the ancient life, natural urges are both emotional as well as physical were given prime importance, these urges were considered as indicators of the immediate needs of the body, expressed through natural urges. In ayurvedic classical texts have explained the salient feature of Mutrakruchra as „Dukhen Mutra pravrutti’´[1]” any type of dukh or discomfort during micturition is included under Mutrakruchra. The learned Ayurvedic Aacharyas have described in details about anatomy, physiology, pathology and symptomatology along with treatment of the disorders of Mutravaha strotas. In this regard Maharshi Sushrut has described that any kind of infection of mutravaha strotas leads to Mutrakruchra (cystitis).”[2]
DISEASE REVIEW
Ayurveda Review--
MUTRAKRUCHHRA:
Vyutpati of Mutrakruchra:
The term mutrakruchra is made up of two words i.e. “Mutra” and“kruchra”
Nirukti: (Defination)
The disease in which urine is passed with difficulty is called Mutrakruchra. In Mutrakruchra pain is a prominent, more than Mutraghata and retention (Vibandha) is less than in Mootraghata. There is constant feeling of urge to void the urine but very little urine is passed.
HETU ( Etiology of Mutrakruchra): [3]
1) Aahariya-(Dietary Factors): Teekshna Aahar and Aushadhi:
2) Viharya – (Physical Factors): Physical exercise
- Aagantuj Hetu (Traumatic Factors):
Types of Mutrakruchra: [4],[5],[6],[7]
Acharya Charaka has described 13 types of Urinary disorders and termed collectively as Mutradosha and also giving separate chapter as Mutrakruchra with its? 8 subtypes.
Similarly, Sushruta has also described 12 types of urinary disorders and termed collectively, as Mootraghata while giving a separate chapter on Mutrakruchra with its 8
Urinary Tract Infections
(Modern Review)
Urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary tract. Although urine contains a variety of fluids, salts, and waste products it does not usually have large no of bacteria in it. When bacteria get invade into the bladder or kidney through urinary tract and multiply in it, further spreads and leads to urinary tract infection. Urinary tract infection are worldwide incidence of approximately 150 million cases annually.
Etiology:-
Urine is normally sterile- that is, it does not normally contain bacteria. Usually several things keep bacteria out of the urine. These includes –
1) The urethral sphincter: when the urethra is squeezed shut, bacteria cannot climb up the urethra from the "meatus" (the outside opening) into the bladder.
2) The length of the urethra: it's a long way up to the bladder for a bacterium. (Since a woman's urethra is shorter than a man's, women are much more likely than men to get UTI's.)
- Frequent washing: any bacteria that make it into the urethra are flushed out the next time of micturition urinate, and since bladder empties almost completely when person does urinate any bacteria that get that far will be flushed out too.
Furthermore, there are valves at the points where the ureters enter the bladder to prevent urine from "refluxing" from the bladder to the kidneys, so that even if the bladder and its urine is infected the bacteria shouldn't travel up to the kidneys.
Factors associated with acute urinary infection include the following:
1) Alcohol consumption
2) Allergy or cold medications containing decongestants or Anti- histamines
3) Certain prescription drugs (e.g. Ipratropiumbromide, Albuterol, Epinephrine) that cause the urethra to become narrow.
4) Delaying urination for a long time
5) Long period of inactivity or bed rest
6) Prolonged exposure to cold temperatures
7) Spinal cord injury/nerve damage
MATERIAL AND METHODS:-
Clinical Trial
Total 60 patients of Pittaj Mutrakruchra were randomly allocated into two equal groups from which 30 patients was taken into Group
A (Trial group) and 30 patients allotted in Group B (control group)
(a) Inclusion criteria -
1) Patients age between 25 to 50 years.
2) Patients having clinical symptoms of Pittaj Mutrakruchra
(Cystitis) like burning sensation, Increase in frequency, Pain
during micturition.
- Both sex were taken.
(b) Exclusion criteria-
1) Pregnant women, History of trauma:-related to urethra, Malignancy and other systemic disorders, Sexually Transmitted Diseases, Calculi, Ureterovesical junction (UVJ) obstructed,Urethral stricture(BPH, injury, congenital, introduce of catheter or cystoscope)
Psychological disorders, Frank Haematuria, Urinary tract infections excluding acute cystitis, ARF, CRF
(c) Withdrawal criteria-
(1) If patient develop any adverse effect.
(2) If patient is not responding to treatment and aggravation of symptoms.
(3) If patient refuses to continue with the treatment.
INSTRUMENT- Foley?s catheter- Female-14 no ,Male-16 no, Syringe-10 ml and 20 ml,Sterile Bowl ,
Sterile cotton, gauze piece 5-7,Artery forcep, Sponge holder ,Sterile gloves , Betadine solution
Poorvakarma- 1) Emptying bladder before Uttarbasti
2) Procedure explained and Written consent being taken
3) Blood pressure and pulse rate were monitored
4) Supine position was given to the patient
Pradhankarma- 1) Uttarbasti with medicated ghruta
- Patient was kept in same position for 15 minutes
Paschatkarma-1) Post procedure blood pressure and pulse rate were recorded
3) Patient was instructed not to pass urine for next 30-45 min
Criteria For Assessment of Result:
- SUBJECTIVE: Sashool mutrapravrutti (Painful micturation) and Sadaha mutrapravrutti (Burning micturation)
|
SIGN |
SCORE |
|
Absent (Before/during/after) |
0
|
|
Present (Before/during/after) |
1
|
- Muhurmuhu mutrapravrutti (Urgency of micturation)
|
SIGN |
GRADE |
SCORE |
|
1-5 times/day |
0 |
0 |
|
5-10 times/day |
+ |
1 |
|
10-15 times/day |
++ |
2 |
|
More than 15 times/day |
+++ |
3 |
- Objective Criteria:
- No. of pus cells-
|
No.of Pus cells |
GRADE |
SCORE |
|
0-5 /hpf |
0 |
0 |
|
6-10/hpf |
+ |
1 |
|
11-15/hpf |
++ |
2 |
|
>16 /hpf |
+++ |
3 |
- No. of R.B.C.-
|
No. Of R.B.C. |
GRADE |
SCORE |
|
0-5 /hpf |
0 |
0 |
|
6-10/hpf |
+ |
1 |
|
11-15/hpf |
++ |
2 |
|
>16 /hpf |
+++ |
3 |
- Litmus paper test
|
Colour change |
1 |
|
No Colour change |
0
|
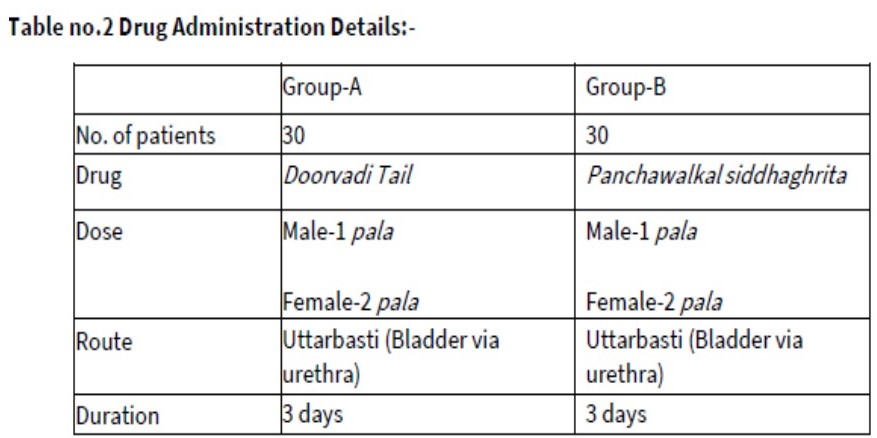
Table no.2 Drug Administration Details:-
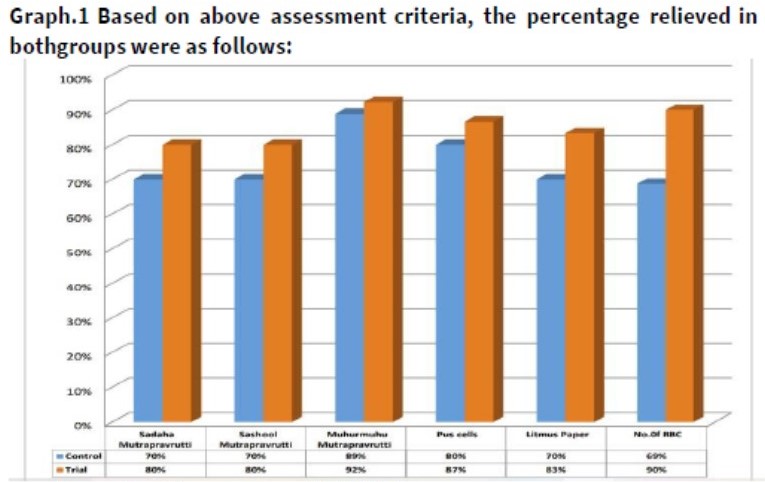
Graph.1 Based on above assessment criteria, the percentage relieved
Observations and Results:
Total 60 patients were taken. Which were divided into two groups Group A & Group B. Each group consist of 30 patients, which were further observed with following 3 different points for the clinical assessment.
- Before treatment (BT)
- Day 3
- After treatment (AT)
Vital Statistics:-
- Age, Gender, Frequency analysis was done based on following demographic points:- Marital Status, Religion, Occupation, Diet
- Clinical Parameters:-
Efficacy of Gokshur siddha ghrita and Panchawalkal siddha ghrita was tested based on the following assessment criteria:-
- Sadaha mutrapravruti (Burning micturation)
- Sashula mutrapravruti (Painful micturation)
- Muhurmuhu mutrapravruti (Urgency of micturation)
- No of RBC
- Litmus paper test
- No of pus cell
Primary End-point:- First 3 days daily uttarbasti was given and observations had done as per clinical assessment criteria. Because symptoms of mutrakruchra (IC) were maintained if management taken properly in first 3 days
Assessment Criteria:
- Efficacy testing of the treatment of Trial and Control Groups were performed by using Wilcoxon Signed Rank (W) test.
- Z-test for proportion of present before treatment and after treatment.
The frequency distribution of demographic data was done
Discussion
Sadaha mutrapravrutti:-Relief in Sadaha mutrapravrutti after treating the patients in Trial group was significant than control group.Sashulamutrapravrutti:-Relief in Sashulamutrapravruti after treating the patients in Trial group was significant than control group.
Muhurmuhumutrapravruti:-Relief in Muhurmuhu mutrapravruti after treating the patients in Trial group was significant than control group.
No of pus cell:-Decrease in no. of pus cell after treating the patients in trial groups was significant than control group.
No of RBC:-Decrease in no. of RBC after treating the patients in trial groups was significant than control group. Litmus paper test:-Litmus paper test after treating the patients in trial groups was significant than control group.
Mode of Action of Doorva--[10]
The Plant Is Astringent, Sweet, Cooling, Haemostatic, Diuretic and Tonic & its pharmacological actions are Antibiotic, Hypertensive, Diuretic, Antilithic, Anticancer, Haemostatic, Antimicrobial & Anti oxidant.
Mode of action of Darvi--
The plant is tonic, stomachic, Astringent, Antiperiodic, Diaphoretic, Antipyretic, Alterative, Emmenogogue & its pharmacological actions are Anticancer, Antifatigue, Antipyretic, Local Anaesthetic, Antituberculer, Antibacterial, Anti-Inflammatory, Hypotensive, Antitumor, Anti Protozoal, Antitrachoma, CNS Depressant
SCOPE FOR STUDY-
Effect of Doorvadi tail can be used in the treatment of various vrana( Wounds),Parikartika(Fissure in Ano),Nadivrana(Sinuses) due to its anti-inflammatory, Astringent, Sweet, Cooling, Haemostatic, Antipyretic, Local Anaesthetic, Antituberculer, Antibacterial properties.
Conclusion
With results observed in patients and with statistical analysis it is observed that doorvadi taila Uttarbasti is useful in treating IC. For Sashula mutrapravruti, No.of Pus cells, No. of RBC,Litmus paper test, Sadaha mutrapravruti, Muhurmuhu mutrapravrutti % of relief for trial group was high as compare to control group. Hence the final conclusion that can be drawn is –Cure of Mutrakruchra ith “Doorvadi tail Uttarbasti” is more effective than Panchawalkal siddha ghruta.
References
- Bhav prakash Nighantu, Krushnachandra, Chunekar, Chaukham baPrakashan, Reprin: year 2013,3/45,46-279
- Charak samhita, Aacharya Vidyadhar Shukla & Prof. Ravi Dutta Shasti, Chaukhamba Prakashan,19th Edition 1993,Chikitsa sthan,26/32-628
- Charak samhita, Aacharya Vidyadhar Shukla & Prof. Ravi Dutta Shasti,Chaukhamba Prakashan,19th Edition 1993,Chikitsa sthan,26/33-629
- Charak samhita,Aacharya Vidyadhar Shukla & Prof. Ravi Dutta Shasti,Chaukhamba Prakashan,19th Edition 1993,Chikitsa sthan,26/34-629
- Charak samhita,Aacharya Vidyadhar Shukla & Prof. Ravi Dutta Shasti,Chaukhamba Prakashan,19th Edition 1993,Chikitsa sthan,26/49-632
- Agnivesa, dridhabala, charaka, caraka samhita, ayurveddeepika commentary, vol.3, siddhi sthana, kalpanasiddhi adhyay, 1/38, edited by kaviraj shree narendranath senagupta and kaviiraj shree balaichandra senagupta, kalikatanagarya publication, kolkata, 1850:3647.
- Vagbhata, ashtang hridaya, by sarvangasundara commentary of arundatta and ayurvedrasayana of hemadri, sutra sthana, Bastividhi adhyaya, 19/2, edited by pr bhishagacharya harisastri paradkar vaidya, 6th ed, bublished by pandurang jawaji nirnaya sagar press, bombay, 1989: 270.
- Vagbhata, ashtang hridaya, by sarvangasundara commentary of arundatta and ayurvedrasayana of hemadri, sutra sthana, shalyaharanavidhi adhyaya, 28/2, edited by pr bhishagacharya harisastri paradkar vaidya, 6th ed, bublished by pandurang jawaji nirnaya sagar press, bombay, 1989: 334.
- www.drugs.com cited on 28.09.2021
- www.webmed.com cited on 23.10.2021

