Case Report
Year: 2022 |Volume: 3 | Issue: 02 |Pages: 42-47
Role of Ayurvedic protocol in successful improvement of post-operative Fournier’s Gangrene- A case study.
About Author
Correspondence Address:
Dr. Ashok Devidas Pawar Associate Professor of Shalyatantra Department, MES Ayurved College & Research Centre, Lote- Ratnagiri, Maharashtra Email : dr.ashok2575@yahoo.com Mob. No. 98222 85836
Date of Acceptance: 2022-02-15
Date of Publication:2022-03-08
Article-ID:IJIM_149_03_22 http://ijim.co.in
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: Nil
How To Cite This Article: Pawar A .D., Borse N.V. Role of Ayurvedic protocol in successful improvement of post-operative Fournier’s Gangrene- A case study. Int J Ind Med 2022;3(2):42-47 http://doi.org/10.55552/IJIM.2022.2306
Abstract
Fournier's gangrene (FG) is a mixed infection caused by both aerobic and anaerobic bacterial flora. The development and progression of the gangrene is often fulminating and can rapidly cause multiple organ failure and death. Because of potential complications, it is important to diagnose the disease process as early as possible Although antibiotics and aggressive debridement have been broadly accepted as the standard treatment, the death rate remains high. Post-operative management remains another major concern as it takes a lot of duration for complete healing. This paper highlights the role of Ayurvedic protocol in a complicated case whereas complete results were achieved in a less time span.
Keywords: Fournier’s Gangrene, Debridement, Vrana dhavana, Vrana dhupana, Vranakarma
Introduction
Fournier's gangrene (FG) is a rare but life-threatening disease. Fournier's gangrene is an infective necrotizing fasciitis that affects the external genitalia, perineal, or perianal regions and can be fatal most usually affects men.[1] In the therapy of FG, early surgical debridement of necrotic tissues and antibiotics are critical. Despite advanced therapy, mortality remains high, ranging between 20% and 30%.[2] Anorectal or urogenital and perineal trauma, including pelvic and perineal injury or pelvic interventions are other causes of FG.[3] Diabetes mellitus is found in 20%–70% of individuals with FG, [4] and chronic alcoholism is present in 25%–50% of patients with FG.[5] The clinical features of Fournier's ganglia include sudden pain, weakness, paleness, and fever in the scrotum. Initially only the scrotum is affected, but if left unchecked, cellulitis will spread until the entire scrotum is peeled off and the testicles will remain exposed and healthy.[6]
Comorbid risk factors for the development of Fournier's gangrene-
-
Diabetes
-
Alcohol misuse
-
Immunosuppression
-
Chemotherapy
-
Chronic corticosteroid use
-
HIV
-
Leukaemia Liver disease
Differential diagnosis of Fournier's gangrene[7]
-
Cellulitis
-
Strangulated hernia
-
Scrotal abscess
-
Streptococcal necrotising fascitis
-
Vascular occlusion syndromes
-
Herpes simplex
-
Gonococcal balanitis and oedema
-
Pyoderma gangrenousm
-
Allergic vasculitis
FG requires aggressive multimodal treatment, including hemodynamic stabilization, broad spectrum antibiotics, and surgical debridement. It must be emphasized, however, that surgical debridement is the primary component of treatment, and if delayed, will adversely affect the prognosis.[8]
CASE HISTORY-
A 60 years old Male patient was brought to the OPD with complains of swelling and pain over scrotal and penile area along with history of fever 2 days back.
Past History: no any surgical history.
Past Medicinal history – not specific
Local examination -
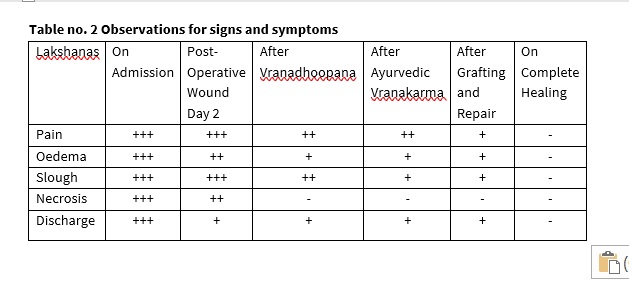
A gross swelling over scrotal and penile region was observed. It was observed that there was increased localized temperature at lesion area. There was Peripheral induration and slough with purulent discharge through perineal region was also present at the time of examination.
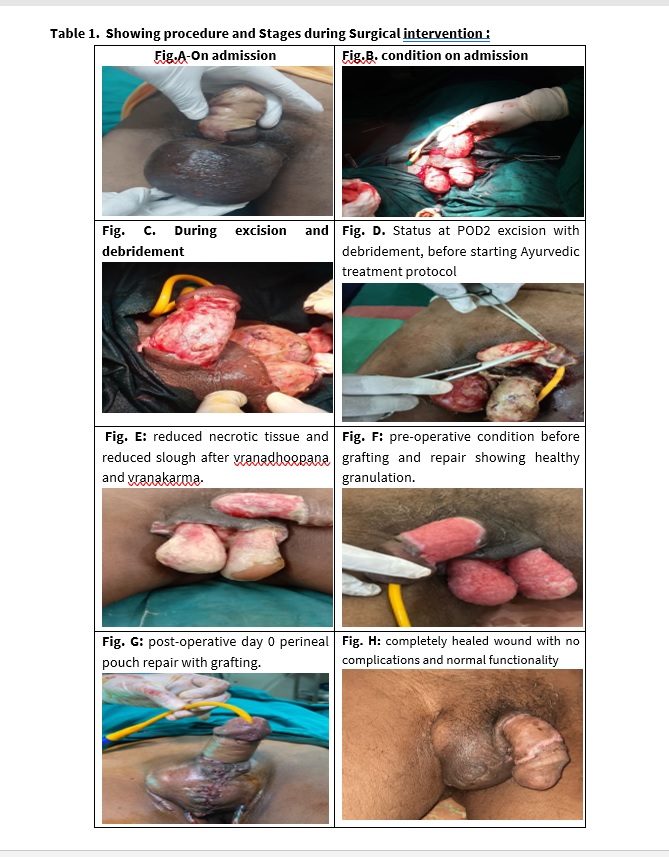
Surgical Management: Debridement of the non-viable tissue was done under spinal anaesthesia, followed by IV antibiotics. After successful achievement of granulation, skin grafting and secondary closure of scrotum was performed under spinal anaesthesia.
The following Ayurvedic protocol was followed-
- Vrana dhavana (irrigation) was done with Triphala decoction.
- Vranakarma (dressing) was done using Nimba Taila and Vranashodhana Taila.
- Vranadhupana (fumigation) was done with coarse powders of: Shunthi (zingiber officinale), Raal (canarium strictum), Agaru (Aquilaria agallocha), Vacha (Acorus Calamus).
- Orally, Triphala guggulu, Gandhak Rasayana and Chandraprabha Vati along with standardised treatment protocol.
- After the grafting and repair, Jatyadi Ghrita was used for Vranakarma.
charts
tables
Discussion
Vranadhupana which means fumigation using dravyas like ghee, vacha, raal etc as described in texts are responsible for reducing secretions and pain (as dhoopan is mainly indicated in vataj, tivra shoolayukta, sravi vrana). Vranakarma which included lekhana which facilitated granulation formation as superficial adherent slough was removed. Shodhana taila and ghrita dressings made the wound suitable for grafting.Diet plays a major role and specifically in a vranita. Yava, godhuma, jeerna shali, saktu, mudga, dadim, patola, karavellaka etc when included in the diet facilitates speedy recovery.
Conclusion
Ayurvedic Para surgical procedures like vranadhoopana, vrankarma and internal Ayurvedic medicines played a major role in treating the case. Also, wound is always a major concern, but peripheral edema, blackish discoloration. So Ayurvedic protocol-based medications help in early healing and less complications.
References
- Fournier's gangrene. Smith GL, Bunker CB, Dinneen MD Br J Urol. 1998 Mar; 81(3):347-55.
- Paw?owski W, Wro?ski M, Krasnodebski IW Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2004 Jul; 17(97):85-7.
- Eke N. Fourniers gangrene: a review of 1726 cases. Br J Surg 200087718–728. [PubMed]
- Morpurgo E, Galandiuk S. Fournier's gangrene. Surg Clin N Am 2002821213–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton M D, Fowler J E, Jr, Sharifi R.et al Causes, presentation and survival of fifty?seven patients with necrotizing fasciitis of the male genitalia. Surg Gynecol Obstet 199017049–55.
- Russell RCG, Williams NS, Bulstrode CJK. Bailey & Love's Short Practice of Surgery. Arnold; 2000.
- Thwaini A, Khan A, Malik A, et al. Fournier's gangrene and its emergency management. Postgrad Med J. 2006;82(970):516-519. doi:10.1136/ pgmj.2005.042069
- The microbiology of necrotizing soft tissue infections. Elliott D, Kufera JA, Myers RAAm J Surg. 2000 May; 179(5):361-6.

