Review Article
Year: 2020 |Volume: 1 | Issue: 7 |Pages: 237-252
Critical Study of Graha (Planet) Dhatu (Tissue) Relationship And Diseases Caused By Them In Ayurveda & Jyotish Science
About Author
Correspondence Address:
Dr. Subhash D. Waghe, M.D.(Roga Nidana) HOD – Dept. of Roga Nidana & Vikruti Vigyana Jupiter Ayurvedic College, Nagpur – 441 108 E-mail – carenidan@rediffmail.com (contact no. 7038000648)
Date of Acceptance: 2020-10-26
Date of Publication:2020-11-02
Article-ID:IJIM_32_11_20 http://ijim.co.in
Source of Support: NIL
Conflict of Interest: NIL
How To Cite This Article: Waghe S.D. Critical Study of Graha (Planet) Dhatu (Tissue) Relationship And Diseases Caused By Them In Ayurveda & Jyotish Science. Int. J Ind. Med. 2020;1(7):237-252
Abstract
Ayurveda and Jyotish science are complimentary to each other and have incorporated concepts of each other. The review of Jyotish literature had showed that malefic planets causes specific diseases based upon their position in particular horoscope. It is observed that the planets also represent the particular dhatus mentioned in Ayurveda (Surya = Asthi, Chandra = Rakta, Mangal = Majja, Budha = Rasa, Guru = Meda, Shukra = Shukra, Shani = Mamsa). The review of Ayurvedic literature showed that there are seven dhatus viz. Rasa (Plasma), Rakta (Blood), Mamsa (Muscles), Meda (Fat), Asthi (Bones) , Majja (Bone marroe and nervous tissue) and Shukra (Semen with sperms) which forms the various tissue of the body and supports the body. In Ayurveda they are also called as ‘Dooshyas’ as they get vitiated by doshas. Ayurveda had described the Dhatu dushtijanya diseases. Attempt has been made to study the interrelation between Graha induced diseases and Dhatu dushtijanya diseases. It is concluded that there exists a definite interrelationship between malefic Graha induced diseases mentioned in Jyotish science and Dhatu dushtijanya diseases mentioned in Ayurvedic science.
Keywords: Malefic Graha induced diseases, Dhatu dushtijanya diseases
Introduction
The review of Jyotish literature had showed that malefic planets causes specific diseases based on their position in particular horoscope. It is observed that the planets also represent the particular dhatus mentioned in Ayurveda (Surya = Asthi, Chandra = Rakta, Mangal = Majja, Budha = Rasa, Guru = Meda, Shukra = Shukra, Shani = Mamsa). The review of Ayurvedic literature showed that there are seven dhatus viz. Rasa (Plasma), Rakta (Blood), Mamsa (Muscles), Meda (Fat), Asthi (Bones) , Majja (Bone marrow and nervous tissue) and Shukra (Semen with sperms) which forms the various tissue of the body and supports the body. In Ayurveda they are also called as ‘Dooshyas’ as they get vitiated by doshas. Ayurveda had described the Dhatu dushtijanya diseases. Attempt has been made to study the interrelationship between Graha induced diseases and Dhatu dushtijanya diseases.
MATERIAL & METHOD
Literary analytical and observational method of research was adopted in the present study. Critical and comparative study of Ayurvedic literature and Jyotish science literature was done to come to rational conclusion.
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Review of Ayurvedic Literature
Rasa Dhatu Dushti Janya Diseases
Rasa Dhatu Dushti Janya diseases are Ashraddha (Aversion towards food), Aruchi (Anorexia), Asya Vairasyam (Change of mouth taste), Hrullas (Nausea), Arasgyat(Loss of taste), Gauravam (Stiffness in body), Angamarda (Bodyache), Tandra (Drowsiness), TamaHa (Fainting), Jwara (Fever), Pandutwam (Pallor), Strotasam Rodha (systemic Obstructions), Klaibyam (Impotence), Sada ( fatigue), Krisha Angata (wasting) , Nasho AgneHe , (Anorexia) , Ayatha Kalam Walay (Untimely wrinkles) , Ayatha Kalam Palitani (Untimely graying of hairs). [1]
Rakta Dhatu Dushti Janya Diseases
Rakta Dhatu Dushti vitiated diseases are Asrukdara ( Menorrhagia), Guda Pakaha (Anal Abscess) Medhraha Pakaha (Urethral abscess), Kushtha (Skin diseases), Visarpa (Erisepals), Pidaka (Boils), Raktapittam (Hemolysis), Aasya Pakaha (Mouth abscess), Pleeha vruddhi (Spleeno-megaly), Raktaj Gulma (Hematometra), Vidradhi (Abscess), Nilika (Bluish discoloration), Kamala (Hemolytic jaundice), Vyanga (Chloasma), Tilkalaka (Moles), Dadru (Ringworm), Charmadala (Psoriasis), Shwitram (Vitiligo), Kotha (Urticaria), Pama (Scabies) [2] and Astramandalam (Echymosis).
Mamsa Dhatu Dushti Janya Diseases
Meda Dhatu Dushti Janya diseases are AdhiMamsa (Gum Malignancy), Arbuda (Malignant tumour), Keela (Corn) , Gala Shaluka (Adenoidal Growth), Gala Shundika (Uvular malignancy), Puti Mamsa (Muscular Suppuration), Alaji (Cyst), Ganda (Tumour), Gandamala ( Lymphadenitis), Upjivhika (Ranula). [3]
Meda Dhatu Dushti Janya Diseases
Meda Dhatu Dushti Janya diseases are Granthi (Cyst), Vruddhi (Growth), Galaganda (Goitre),
Arbuda (Tumour), Medoj Aushthaprakopa (Lip lipoma), Madhumeha (Diabetes), Ati Sthaulya (Obesity), Ati Sweda (Sweating). [4]
Asthi Dhatu Dushti Janya Diseases
Asthi Dhatu Dushti Janya diseases are Adhi Aasti (Extra bones), Adhi Dantau (Extra Tooth),
Asthi Bhedam (Arthralgia), Danta shoolam (Dental pain), Vivarnata (Discolouration), Kesha Dosha (Hair disorders such as alopecia), Nakha Dosha (Nail problems such as brittleness). [5]
Majja Dhatu Dushti Janya Diseases
Asthi Dhatu Dushti Janya diseases are Ruk Parwanam (Joint pain), Bhramo (Vertigo), Murchha (Fainting), Adarshanam (Syncope), Arunsham Parwajanam (Tophies on joints). [6]
Shukra Dhatu Dushti Janya Diseases
Shukra Dhatu Dushti Janya diseases are Klaibya (Impotence), Aharshanam (Loss of libido), Rogi Wa Virupam (children affected with genetic defects), Alpa Ayu Prajayate (children are short lived), Prastravati Patati (Miscarriage & Abortions), Na Jayate Garbha (Infertility), Klibam Prajayate (Impotancy in children), Apatyam Badhate (infertility in children), Daurbaly (Weakness), Shrama (Fatigability), Pandutwa (Pallor), Mukhashosha (Atrophy of cheeks), Shukra Avisarga (Ejaculatory failure). [7]
Review of Jyotish science Literature
Interelationship of Dhatus And Grahas
The Rasa dhatu is ruled by planet Budha (Mercury). The Rakta dhatu is ruled by planet Chandra (Moon). The Mamsa dhatu is ruled by planet Shani (Saturn). The Meda dhatu is ruled by planet Guru (Jupiter). The Asthi dhatu is ruled by planet Surya (Sun). The Majja dhatu is ruled by planet Mangal (Mars). The Shukra dhatu is ruled by planet Shukra (Venus). [8]
Diseases caused by Grahas
Diseases Due to Malefic Surya (Sun)
The diseases due to malefic effects of Sun are Jwara (fever), Patan (fall from height/Traumatic disease), Apasmara (epilepsy) , Hritroga (heart disorders) , Krod Rogas , (liver diseases) Druk Rogas (Eye diseases), Twak /Kushtha dosham (skin diseases), Asthi vikara (bone disorders), Bhuta avesha (microbial infections), Visha Vikara (Poisoning) [9] [10]
Diseases Due to Malefic Chandra (Moon)
The diseases due to malefic effects of Moon are Nidra (sleepiness), Aalasya (lassitude), Kapharoga (hyperlipidimic states), Agnimandya (decreased in appetite), Atisara (loose motions), Pitaka (papule, boil), Sheeta Jwara (fever with chill), Kamala (Jaundice), Rakta-Vikara (blood disorders), Kushata (skin diseases), Balagraha (microbial infections. [11][12]
Diseases Due to Malefic Mangal (Mars)
The diseases due to malefic effects of Mangal (Mars) are, Trishna (thirst), Rakta Prakopa (vitiation of blood) , Pitta Jwara (Inflammatory fevers), Kushtha (skin diseases) , Netra Roga, (eye diseases) Gulma (tumours) , Apasmara (epilepsy), Parushta (dryness) , Deha-bhanaga (fractures), Raksha Gandharva Graha Rogas (microbial infections of blood and bone marrow).[13] [14]
Diseases Due to Malefic Budha (Mercury)
The diseases due to malefic effects of Budha (Mercury) are Bhranti (vertigo), Netra Vikara (Eye diseases) , Gala Vikara (Throat diseases), Ghrana Vikara (Nasal diseases), Jwara (fever), Pitta-Kaphaj Vikara, Pandu (anemia), Twacha Vikara (skin diseases), Vicharchika (eczema) , Gandharva Graha Pida (microbial infections of Ear Nose Throat). [15] [16]
Diseases Due to Malefic Guru (Jupiter)
The diseases due to malefic effects of Guru (Jupiter) are Gulma (abdominal tumour) , Antra Jwara (enteric fever), Kapha Rogas (hyperlipidimic diseases), Shrotra Rogas (diseases of Ear), Prameha (diabetes) , Shoka (depression), Kinnar Yaksha Deva Graha Pida (microbial infections of gastrointestinal tract). [17] [18]
Diseases Due to Malefic Shukra (Venus)
The diseases due to malefic effects of Sun are Kapha-Vataj Rogas , Pandu (anemia) , Netra Vikara (Ophthalmic diseases) , Aasya Vikara (diseases of mouth), Shrama (fatigue) , Guhya Rogas (genital disorders), Mutrakrichhra (dysuria) , Shukra Struti (premature ejaculations), Yogini Matruka Graha Pida (microbial infections of genito-urinary tract). As per Gadavali , the malefic Shukra also leads to Ganikottha vikara (sexually transmitted diseases), Pandu (anemia), Prameha (polyuria), Shosha (emaciation) apart from above said diseases.[19] [20] [21]
Diseases Due to Malefic Shani (Saturn)
The diseases due to malefic effects of Shani (Saturn) are Vata-Kaphaj Vikara, Tandra (drowsiness), Shrama (fatigue) , Bhranti (vertigo), Kukshi Ruk (pain in loins), Pishacha Graha Pida (microbial infections of muscles, bones and brain). As per Gadavali, malefic Shani also leads to Sandhirogas (joint disorders), Guhya roga (undiagnosable diseases), shwas rogas (breathing disorders) apart from above said diseases.[22] [23] [24]
Diseases Due to Malefic Rahu & Ketu (Dragon’s head & Tail)
The diseases due to malefic effects of Rahu and Ketu are Tapa kara/Jwara (fever) , Kushtha (skin diseases), Visha (poisoning), Pishach , Preta, Sarpa Graha Badha (microbial infections).[25] [26] [27]
Understanding Disease Potential of Grahas
The disease causing potential of grahas should be decided from their position in 6th, 8th, and 12th houses of the birth chart.
Clinical Application of Graha Dhatu Disease Concept As Per Jyotisha
The diseases caused by vitiation of dhatus gets alleviated by worshipping that particular dhatu related planet with Japa (enchanting the Graha Mantra), Tarpana (offering the water and food to the Graha), Homa (Paying oblations to the Graha), Dana (Paying donations to the Graha).
In Ayurveda, diseases caused by vitiation of dhatus are treated with various drugs. In case of failure to drug therapy then above said Jyotishokta measures are adopted as a part of ‘Daiva Vyapashraya’ treatment. [28]
OBSERVATIONS
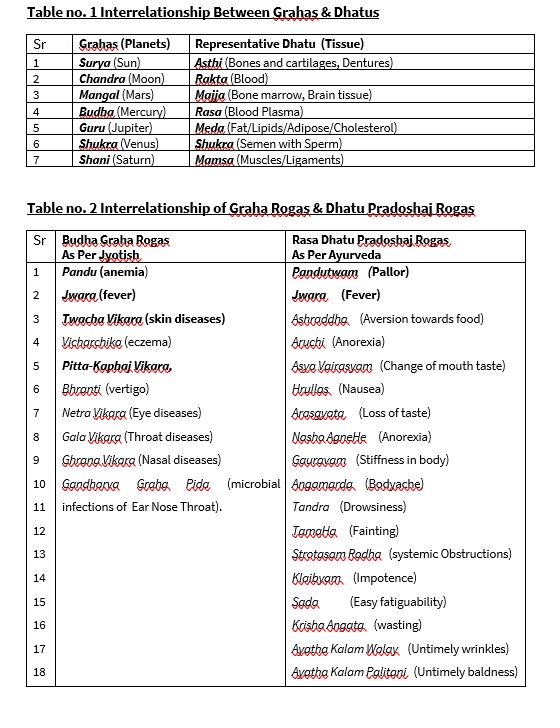
table no. 1 and 2
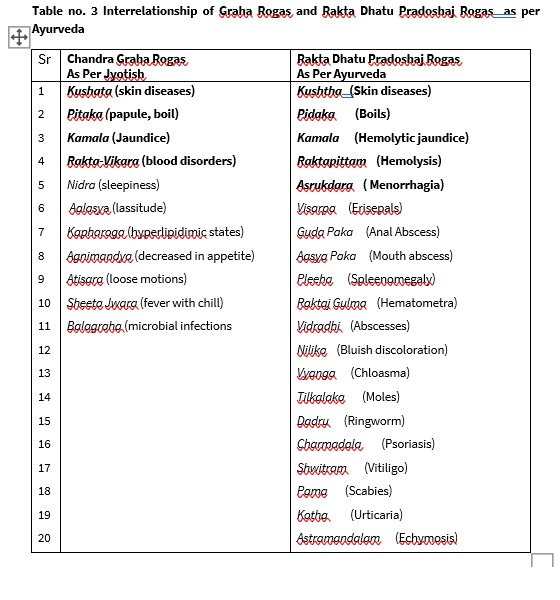
table no. 3
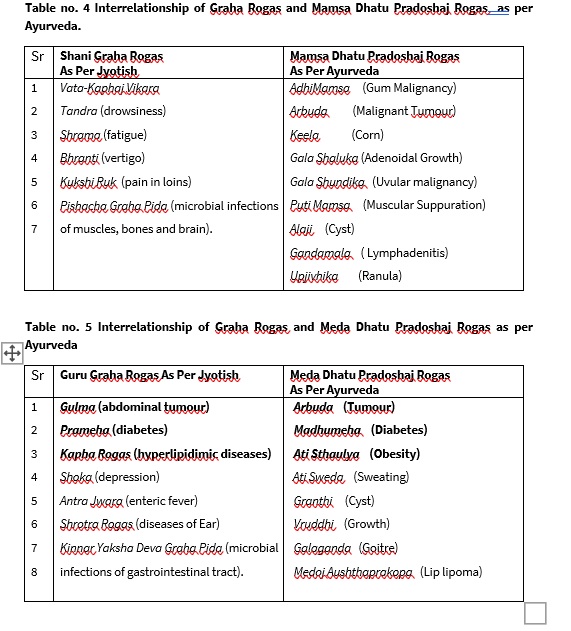
table no. 4 and 5
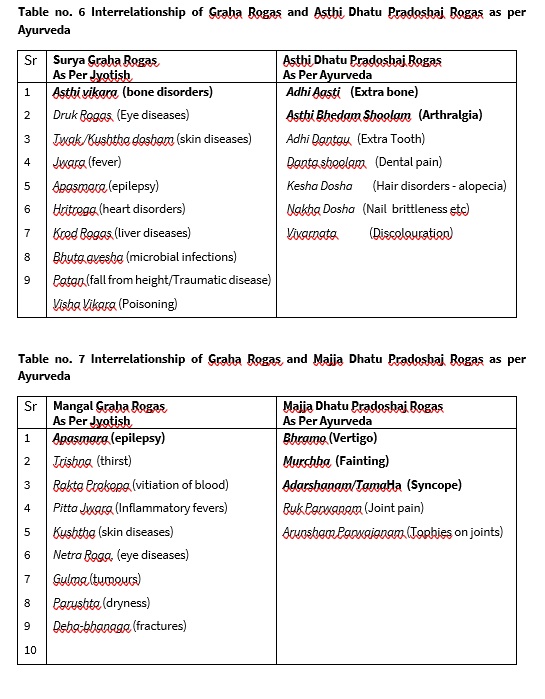
table no. 6 and 7

table no.8
Discussion
As per Ayurveda, Rasa-dhatu though flows in blood vessels, mainly is Twakgata i.e. mainly reflects in skin. Hence, Rasadhatu dushti is readily evident on skin. Anemia is one such condition where paleness is reflected on skin. Pandu (anemia) has been mentioned as the Rasa dhatu dushtijanya vikara in Ayurveda. Rasa dhatu as per Jyotish science is represented by Budha (mercury) planet and malefic effect of Budha also give rise to Pandu (anemia). As per Jyotish science, Kushtha (skin diseases) and Vicharchika (eczema) also manifest due to malefic effect of Budha which is quiet obvious from the fact that Rasadhatu dushti mainly reflects in skin. Similarly, Jwara (fever) is also mentioned as one of the manifestation of Rasadhatu dushti by Ayurveda. In Jyotish science, also Jwara (fever) is mentioned as the malefic effect of Budha. Hence, there is similarity in the opinion of both the sciences. Ayurveda had mentioned many other gastrointestinal features of Rasadusti as being the first ever dhatu to be formed by Agni during metabolism. Jyotish science had summarized these features by calling it as Pitta Kapha janya vikaras which covers almost all of them. Pitta represents the Agni and Rasa dhatu is mainly Kaphaj in nature. Thus, interrelation between the Budha Graha and Rasa dhatu is proved.
As per Ayurveda, Rakta-dhatu though flows in blood vessels and is formed in liver and spleen. In Jyotish science, Rakta dhatu is represented by Chandra (moon). One of the manifestation of Rakta dhatu dushti is Kamala (hemolytic jaundice). As per Jyotish science, also one of the malefic effect of Chandra is Kamala (hemolytic jaundice). Kushtha (skin diseases) and Pitaka (boil) are the common manifestation of Raka dushti and malefic effect of moon mentioned by Ayurveda and Jyotish science respectively. Ayurveda had mentioned several other Rakta dushtijanya vikaras (diseases) which have been summarized by Jyotish science as Raktajanya Vikaras (blood disorders). Thus, interrelation between the Chandra Graha and Rakta dhatu is proved.
In Jyotish science, Shani (Saturn) represents the snayu. Although, Snayu is correlated to Mans Snayu but there is other class of Ayurvedic peoples, especially Bengal tradition, who correlate snayu with nerves. Hence, there is discrepancy in features related to this particular graha and the dhatu it represent. In Ayurveda, mainly Mans Dhatu Prdhan vikruti like Arbuda (tumour), Granthi (Cyst) etc are mentioned whereas in Jyotish science, the neurological abnormalities are attributed to malefic Shani. Also from Jyotishiya point of view, Shani is Vata Pradhan and gaseous in nature. As per Ayurveda, Vata causes nervine disorders like paralysis etc. In this context, there is relation between Shani and Vatapradhan majja snayu or Mamsa snayu vikruti.
As per Ayurveda the Ashraysthana of Vata is Asthi. Hence, vitiated Vata also causes diseases of bones and joints. As per Jyotish book, Gadavali, malefic Shani also leads to Sandhigat Vikaras (joint disorders). In Jyotish science, Meda dhatu is represented by Guru (Jupiter). One of the manifestation of Meda dhatu dushti is Prameha (Diabetes). As per Jyotish science, also one of the malefic effect of Guru is Prameha (Diabetes). Arbuda/Gulma (Tumour) is the other common manifestation of Meda dushti and malefic effect of Guru mentioned by Ayurveda and Jyotish science respectively. In jyotish science, malefic Guru is the karaka (leads to) of sthulata (obesity) which is also endorsed by the Ayurveda by calling it a medojanya Vikara. Ayurveda had mentioned several other Meda dushtijanya vikaras (Dislipidemic diseases) which have been summarized by Jyotish science as Kaphajanya Vikaras (Hyperlipidemic states). Thus, interrelation between the Guru Graha and Meda dhatu is proved.
In Jyotish science, Asthi dhatu is represented by Surya (Sun). One of the manifestation of Asthi dhatu dushti is Adhi Asthi and Asthi Bheda (Bone deformity and bone pain). As per Jyotish science, one of the malefic effect of Surya is Asthi Vikaras (Bone disorders) which encompasses wide range of bone disorders. Ayurveda had mentioned several other Asthi dushtijanya vikaras (bone diseases) which have been summarized by Jyotish science as Asthi Vikaras (Bone disorders). Thus, interrelation between the Surya Graha and Asthi dhatu is proved. In Jyotish science, Majja dhatu is represented by Mangal (Mars). One of the manifestation of Majja dhatu dushti is Murchha and Bhrama (Fainting and vertigo). As per Jyotish science, also one of the malefic effect of Mangal is Apasmara (Convulsion and fall). As per Ayurveda, Bhrama and Murchha are Pittaj diseases. One of the manifestation of malefic Mangal is severe Trishna (thirst) which is again feature of aggravated Pitta as per Ayurveda. As per Jyotish science, malefic Mangal causes Pittajanya vikaras. Thus, interrelation between the Mangal Graha and Majja dhatu is proved.
In Jyotish science, Shukra dhatu is represented by Shukra (Venus). One of the manifestation of Shukra dhatu dushti is Pandu (anemia). As per Jyotish science, also one of the malefic effect of Shukra is Pandu (anemia). Whereas Ayurveda mentions Klaibya (impotence) as manifestation of Shukra dhatu dushti, Jyotish science had mentioned Guhya rogas (Genital disorders) as the effect of malefic Shukra. Guhya rogas is broad term used to include all types of Genital disorders. Shrama (Fatigue) is the common symptom mentioned by Ayurvda and Jyotish science of Shukra dushti and malefic Shukra respectively. Ejaculatory failure or premature ejaculation are the features mentioned by Ayurvda and Jyotish science of Shukra dushti and malefic Shukra respectively. Mutrakrichhra (dysuria) is a obvious feature of malefic shukra mentioned by Jyotish science. As per Jyotish book Gadavali, the malefic Shukra also leads to the Ganikottha Vikaras (sexually transmitted diseases). Thus, interrelation between the Shukra Graha and Shukra dhatu is proved. Thus, interrelation between the Shukra Graha and Shukra dhatu is proved.
Conclusion
1. There exists a relationship between malefic Budha (Mercury) induced diseases and Rasa Dhatu (Plasma) dushti induced diseases.
2. There exists a relationship between malefic Chandra (Moon) induced diseases and Rakta Dhatu (Blood) dushti induced diseases.
3. There exists a relationship between malefic Shani (Saturn) induced diseases and Mamsa Dhatu (Muscle) dushti induced diseases.
4. There exists a relationship between malefic Guru (Jupiter) induced diseases and Meda Dhatu (Fat) dushti induced diseases.
5. There exists a relationship between malefic Surya (Sun) induced diseases and Asthi Dhatu (Bone) dushti induced diseases.
6. There exists a relationship between malefic Mangal (Mars) induced diseases and Majja Dhatu (Bone marrow) dushti induced diseases.
7. There exists a relationship between malefic Shukra (Venus) induced diseases and Shukra Dhatu (Semen) dushti induced diseases.
References
value="
- Acharya Vidyadhar Shukla, Ravidutta Tripathi, ‘Charak samhita’ of acharya Charak and agnivesha, Sutrasthana 28/9-10, hindi translation, 1st edition, Vol. 1, published by Chaukhamba Sanskrit Pratishthan, 4360/4, ansari road, Daryaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2019, pg. 429-430
- Acharya Vidyadhar Shukla, Ravidutta Tripathi, ‘Charak samhita’ of acharya Charak and agnivesha, Sutrasthana 28/11, hindi translation, 1st edition, Vol. 1, published by Chaukhamba Sanskrit Pratishthan, 4360/4, ansari road, Daryaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2019, pg. 429-430
- Acharya Vidyadhar Shukla, Ravidutta Tripathi, ‘Charak samhita’ of acharya Charak and agnivesha, Sutrasthana 28/14, hindi translation, 1st edition, Vol. 1, published by Chaukhamba Sanskrit Pratishthan, 4360/4, ansari road, Daryaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2019, pg. 429-430
- Dr. Anantram Sharma,’ Sushrut Samhita’ of acharya Sushruta, sutrasthana 24/9, edited and translated in hindi by Atrideva, 5th edition,Vol.1, published by Chaukhamba Surbharati Publication, Gopal Mandir lane,Varanasi-221001, 2017, pg.205
- Acharya Vidyadhar Shukla, Ravidutta Tripathi, ‘Charak samhita’ of acharya Charak and agnivesha, Sutrasthana 28/16, hindi translation, 1st edition, Vol. 1, published by Chaukhamba Sanskrit Pratishthan, 4360/4, ansari road, Daryaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2019, pg. 429-430
- Acharya Vidyadhar Shukla, Ravidutta Tripathi, ‘Charak samhita’ of acharya Charak and agnivesha, Sutrasthana 28/17, hindi translation, 1st edition, Vol. 1, published by Chaukhamba Sanskrit Pratishthan, 4360/4, ansari road, Daryaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2019, pg. 429-430
- Acharya Vidyadhar Shukla, Ravidutta Tripathi, ‘Charak samhita’ of acharya Charak and agnivesha, Sutrasthana 28/18, hindi translation, 1st edition, Vol. 1, published by Chaukhamba Sanskrit Pratishthan, 4360/4, ansari road, Daryaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2019, pg. 429-430
- Pt. Padmanabh Sharma, Brihat Parashar Horashastra of acharya Parashara, Grahaguna Swarupadhyay 3/32, hindi translation, 1st edition published by Chaukhamba Surbharati Prakshan, Varanasi -221 001, 2018, pg. 10
- Harishankar Pathak, ‘Faladipika’ of Mantreshwara, 14/2 , 1st edition, hindi translation, published by Chaukhamba Surabharati, Varanasi – 221001, pg. 159-161
- Shukadeva Chaturvedi and jagannath Bhasin, ‘Prashna Marga’ of Nambudri Brahmana, 12/67, edited and translated in hindi by, 1st edition published by Ranjan Publications, 16, Ansari Road, Dariyaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2009 , pg. 186-188
- Harishankar Pathak, ‘Faladipika’ of Mantreshwara, 14/3 , 1st edition, hindi translation, published by Chaukhamba Surabharati, Varanasi – 221001, pg. 159-161
- Shukadeva Chaturvedi and jagannath Bhasin, ‘Prashna Marga’ of Nambudri Brahmana, 12/68, 1st edition , edited and translated in hindi by, published by Ranjan Publications, 16, Ansari Road, Dariyaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2009 , pg. 186-188
- Harishankar Pathak, ‘Faladipika’ of Mantreshwara, 14/4, 1st edition, hindi translation, published by Chaukhamba Surabharati, Varanasi – 221001, pg. 159-161
- Shukadeva Chaturvedi and jagannath Bhasin, ‘Prashna Marga’ of Nambudri Brahmana, 12/69, 1st edition , edited and translated in hindi by, published by Ranjan Publications, 16, Ansari Road, Dariyaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2009 , pg. 186-188
- Harishankar Pathak, ‘Faladipika’ of Mantreshwara, 14/5 1st edition, hindi translation, published by Chaukhamba Surabharati, Varanasi – 221001, pg. 159-161
- Shukadeva Chaturvedi and jagannath Bhasin, ‘Prashna Marga’ of Nambudri Brahmana, 12/70, 1st edition , edited and translated in hindi by, published by Ranjan Publications, 16, Ansari Road, Dariyaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2009 , pg. 186-188
- Harishankar Pathak, ‘Faladipika’ of Mantreshwara, 14/6 ,1st edition, hindi translation, published by Chaukhamba Surabharati, Varanasi – 221001, pg. 159-161
- Shukadeva Chaturvedi and jagannath Bhasin, ‘Prashna Marga’ of Nambudri Brahmana, 12/71, 1st edition, edited and translated in hindi by, published by Ranjan Publications, 16, Ansari Road, Dariyaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2009 , pg. 186-188
- Harishankar Pathak, ‘Faladipika’ of Mantreshwara, 14/6 , 1st edition, hindi translation, published by Chaukhamba Surabharati, Varanasi – 221001, pg. 159-161
- Shukadeva Chaturvedi and jagannath Bhasin, ‘Prashna Marga’ of Nambudri Brahmana, 12/72, 1st edition ,edited and translated in hindi by, published by Ranjan Publications, 16, Ansari Road, Dariyaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2009 , pg. 186-188
- Pt. Chakradhar Joshi, Gadavali, 1/12, ,Gadavali 1/12 hindi translation, 1st edition, published by Himalayan Astrological Research Institute, Badrinath -246 422, 1958, pg. 5
- Harishankar Pathak, ‘Faladipika’ of Mantreshwara, 14/8, 1st edition, hindi translation, published by Chaukhamba Surabharati, Varanasi – 221001, pg. 159-161
- Shukadeva Chaturvedi and jagannath Bhasin, ‘Prashna Marga’ of Nambudri Brahmana, 12/73 edited and translated in hindi by, 1st edition published by Ranjan Publications, 16, Ansari Road, Dariyaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2009 , pg. 186-188
- Pt. Chakradhar Joshi, Gadavali, 1/12, ,Gadavali 1/12 hindi translation, 1st edition, published by Himalayan Astrological Research Institute, Badrinath -246 422, 1958, pg. 5
- Harishankar Pathak, ‘Faladipika’ of Mantreshwara, 14/9, 1st edition, hindi translation, published by Chaukhamba Surabharati, Varanasi – 221001, pg. 159-161
- Shukadeva Chaturvedi and jagannath Bhasin, ‘Prashna Marga’ of Nambudri Brahmana, 12/734, 1st edition , edited and translated in hindi by, published by Ranjan Publications, 16, Ansari Road, Dariyaganj, New Delhi – 110 002, 2009 , pg. 186-188
- Dr. Sureshchandra Mishra, Saravali of Kalyan Verma , hindi translation 1/5, 1st edition, published by Ranjan publications, 16, Ansari Road, Dariyaganj, New Delhi 110 002, 2011, pg.27
- Dr. Harishankar Pathak, ‘Jatak Parijat’ of Daivagya Vaidyanath, 2/83, hindi translation , 1st edition, published by Chaukhamba Surabharati, Varanasi – 221001, 2012, pg. 3
"

